
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 Shenzhen Institute for Advanced Study, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Shenzhen 518000, China
3 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, , ChinaHong Kong
4 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, , ChinaHong Kong
Optical scanning holography (OSH) records both the amplitude and phase information of a 3D object by a 2D scan. To reconstruct a 3D volumetric image from an OSH hologram is difficult, as it suffers from the defocus noise from the other sections. The use of a random phase pupil can convert defocus noise into speckle-like noise, which may require further processing in sectional image reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a U-shaped neural network to reduce this speckle haze. Simulation results show that the proposed method works effectively and efficiently both in simple and complex graphics.
digital holography image reconstruction defocus noise neural network Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(8): 080501

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 DTU Fotonik, Technical University of Denmark, DK-2800 Lyngby, Denmark
2 Institute of Mirco/Nano Optoelectronic and Terahertz Technology, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
3 Surrey Ion Beam Centre, Surrey University, Guildford, GU2 7XH, UK
The polarization beam splitter is a key component for polarization manipulation in photonic integrated circuits, but it is challenging to design for low-refractive-index optical materials, due to the low birefringence of the waveguides. We propose what we believe is a novel compact vertical-dual-slot waveguide-based coupling scheme for silicon carbide, enabling efficient low-birefringence polarization splitting by extensively modulating the transverse-magnetic mode distribution. We numerically and experimentally demonstrate the device in the 4H-silicon-carbide-on-insulator integrated platform, with a small footprint of . The device, easy to fabricate via a single lithography process as other components on the chip, exhibits low insertion loss of and for the transverse-electric and transverse-magnetic polarized light, respectively, and polarization extinction ratio of , over 80 nm wavelength range.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(1): 010000A8
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2 Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, Kgs. Lyngby 2800, Denmark
3 Center of Material Science, College of Liberal Arts and Sciences, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
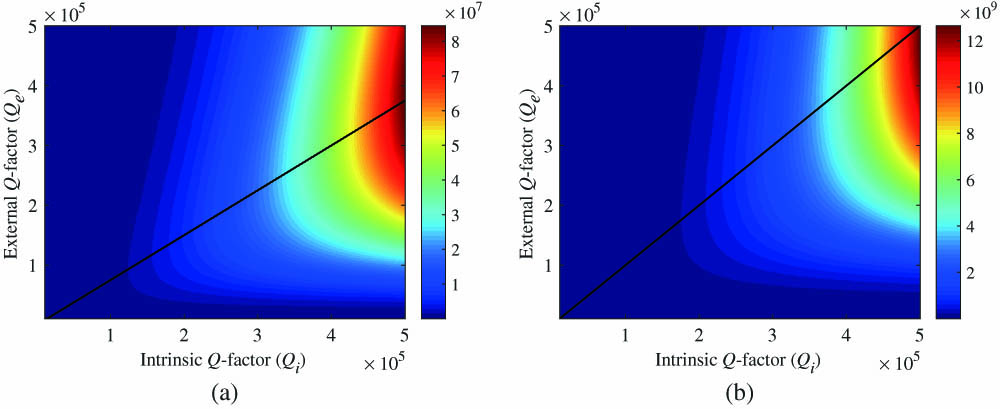
To achieve photon-pair generation scaling, we optimize the quality factor of microring resonators for efficient continuous-wave-pumped spontaneous four-wave mixing. Numerical studies indicate that a high intrinsic quality factor makes high pair rate and pair brightness possible, in which the maximums take place under overcoupling and critical-coupling conditions, respectively. We fabricate six all-pass-type microring resonator samples on a silicon-on-insulator chip involving gap width as the only degree of freedom. The signal count rate, pair brightness, and coincidence rate of all the samples are characterized, which are then compared with the modified simulations by taking the detector saturation and nonlinear loss into account. Being experimentally validated for the first time to the best of our knowledge, this work explicitly demonstrates that reducing the round-trip loss in a ring cavity and designing the corresponding optimized gap width are more effective to generate high-rate or high-brightness photon pairs than the conventional strategy of simply increasing the quality factor.
Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Quantum optics Nonlinear optics, devices Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000587
1 Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, 2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
2 FOTON Laboratory, CNRS UMR 6082, ENSSAT, University of Rennes 1, F-22305 Lannion, France
3 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Wavelength conversion based on degenerate four-wave mixing (FWM) was demonstrated and compared between silicon nanowire and microring resonator (MRR). 15 dB enhancement of conversion efficiency (CE) with relatively low input pump power (5 mW) was achieved experimentally in an MRR. The impacts of bus waveguide length and propagation loss were theoretically analyzed under the effect of nonlinear loss.
wavelength conversion wavelength conversion four-wave mixing(FWM) four-wave mixing(FWM) silicon nanowaire silicon nanowaire microring resonator (MRR) microring resonator (MRR) Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2016, 9(3): 390
1 Department of Photonics Engineering, Technical University of Denmark, 2800 Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark
2 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
3 Department of Microtechnology and Nanoscience, Chalmers University of Technology, Gothenburg, Sweden
4 FOTON Laboratory, CNRS UMR 6082, University of Rennes 1, ENSSAT, 22300 Lannion, France
Silicon micro-ring resonators (MRRs) are compact and versatile devices whose periodic frequency response can be exploited for a wide range of applications. In this paper, we review our recent work on linear alloptical signal processing applications using silicon MRRs as passive filters. We focus on applications such as modulation format conversion, differential phase-shift keying (DPSK) demodulation, modulation speed enhancement of directly modulated lasers (DMLs), and monocycle pulse generation. The possibility to implement polarization diversity circuits, which reduce the polarization dependence of standard silicon MRRs, is illustrated on the particular example of DPSK demodulation.
linear all-optical signal processing linear all-optical signal processing micro-ringresonator (MRR) micro-ringresonator (MRR) polarization diversity polarization diversity silicon-on-insulator(SOI) silicon-on-insulator(SOI) Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2016, 9(3): 362
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong, China
2 Institute of Applied Physics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 610054 Chengdu, China
In optical scanning holography, one pupil produces a spherical wave and another produces a plane wave. They interfere with each other and result in a fringe pattern for scanning a three-dimensional object. The resolution of the hologram reconstruction is affected by the point spread function (PSF) of the optical system. In this paper, we modulate the PSF by a spiral phase plate, which significantly enhances the lateral and depth resolution. We explain the theory for such resolution enhancement and show simulation results to verify the efficacy of the approach.
Digital holography Digital holography Computational imaging Computational imaging Optical transfer functions Optical transfer functions Photonics Research
2016, 4(1): 01000001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong, China
2 Institute of Applied Physics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 610054, Chengdu, China
3 Bradley Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia 24061, USA
The optical scanning holography (OSH) technique can capture all the three-dimensional volume information of an object in a hologram via a single raster scan. The digital hologram can then be processed to reconstruct individual sectional images of the object. In this paper, we present a scheme to reconstruct sectional images in OSH with enhanced depth resolution, where a spatial light modulator (SLM) is adopted as a configurable point pupil. By switching the SLM between two states, different Fresnel zone plates (FZPs) are generated based on the same optical system. With extra information provided by different FZPs, a depth resolution at 0.7 μm can be achieved.
Digital holography Inverse problems Image reconstructionrestoration Computational imaging Photonics Research
2014, 2(2): 02000064





